A crucial economic bond is a relationship between government expenditure and the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). By analyzing the quantity of US government expenditure in proportion to GDP, we may gain crucial information about the status of the US economy. The importance of this ratio, its computation, historical patterns, and its consequences for both policymakers and citizens will all be covered in this blog article.
Â
Overview of US Government Spending
Government expenditure is the term used to describe how much money the US government assigns to various projects, services, infrastructure improvements, and public goods. So, to satisfy the financial demands of the government entails using tax income, borrowing money, and other resources.
Â
Major Categories of Government Spending
Â
Defense Spending: Defense spending represents the financial resources allocated to the military and national security. It encompasses funding for personnel, operations, equipment, research, and development of defense capabilities. To ensure national security and combat preparedness, the US government reserves a large portion of its budget for the military.
Social Programs: Social programs entail government expenditures aimed at providing social welfare and assistance to individuals and families in need. Healthcare, education, housing, unemployment benefits, nutrition aid, and income support programs are just a few of these initiatives. Social programs aim to advance opportunity equality, enhance social welfare, and address societal problems.
Infrastructure Investment: Infrastructure investment involves government spending on the development, maintenance, and improvement of public infrastructure. These include public amenities like roads, bridges, hospitals, airports, and trains as well as communication networks like broadband and the internet and public utilities like electricity and water supplies. Infrastructure investment stimulates economic growth, enhances productivity, and supports job creation.
Research and Development: The US government allocates funds to support scientific research, technological advancements, and innovation. This retains investment in areas like medical research, space exploration, renewable energy, and defense technology. Research and development spending fosters innovation, drives technological progress, and contributes to economic competitiveness.
Â
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Overview
Gross Domestic Product in short GDP is a crucial economic metric that is used to measure the total worth of goods and services produced within the nation's boundaries in a certain period. It provides a comprehensive snapshot of the economic activity within a nation. GDP takes into account the monetary value of all final goods and services, encompassing both tangible products and intangible services. It serves as a yardstick for estimating the overall economic performance and size of an economy.
Â
Basic Components of GDP
Â
Consumption: Consumption refers to the expenditure made by individuals and households on goods and services. Things like food, housing, clothing, healthcare, and transportation fall under consumption spending. Consumer spending acts as a significant driver of economic evolution and is sometimes used to know how the economy of a nation is performing.
Investment: Investment represents the expenditures made by businesses and individuals on capital goods, such as machinery, equipment, and structures, to increase future production and generate income. Investment also includes research and development activities, which contribute to technological advancements and innovation.
Government Spending: All governmental levels, including the federal, state, and municipal, spend money on providing the public with products and services. It encompasses various sectors such as defense, education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social programs. Government spending influences economic activity and can act as a catalyst for economic growth and stability.
Net Exports: Net exports reflect the difference between a country's exports and imports of goods and services. A nation's GDP increases when its exports exceed its imports, generating a trade surplus. Conversely, a trade deficit occurs when imports exceed exports, impacting GDP negatively.
Â
Significance of Comparing Government Spending to GDP
In economic analysis and policymaking, comparing government spending to GDP is highly important. This comparison provides crucial insight into the significance of government spending relative to the whole economy, how it affects economic growth and stability, and how effectively fiscal policy is working as assessed by the proportion of government expenditures to GDP.
Â
Importance of Measuring the Size of Government Spending
Measuring the size of government spending concerning the overall economy is crucial. It allows us to understand the scale of public expenditures and their impact on resource allocation. We can determine how much the government uses economic resources to offer public goods, services, and programs by comparing government spending to GDP. This measurement helps evaluate the scope and reach of government intervention in the economy.
Â
Role of Government Spending In Influencing Economic Growth
Government spending plays a vital role in influencing economic growth and stability. Government spending growth may increase economic activity, increase employment, and increase overall demand. Providing fiscal stimulus during economic downturns, it can also serve as a countercyclical strategy. Government expenditure that is too high concerning GDP, however, can raise issues including budget deficits, inflationary pressures, and the dispersal of private investment. To determine the proper degree of government engagement in the economy and guarantee stable and sustainable growth, it is valuable to analyze the government expenditure to GDP ratio.
Â
Use of the Government Spending-To-GDP Ratio
The government spending-to-GDP ratio serves as an essential indicator of fiscal policy effectiveness. It allows policymakers to evaluate the consequences of government spending on the overall economy. A high ratio may indicate a large fiscal footprint, potentially signaling potential fiscal imbalances, increased debt levels, or inefficient allocation of resources. Conversely, a low ratio may suggest limited public investments or inadequate provision of essential services. Monitoring the ratio of government expenditure to GDP over time assists decision-makers in determining how effective and efficient fiscal policies are, selecting budgetary priorities, and ensuring sound fiscal management.
Â
Calculation of the Government Spending-to-GDP Ratio
One can quickly obtain the ratio of government spending to GDP by using a simple formula to establish the relationship between the spending of the government and GDP. This calculation provides valuable insights into the proportion of the economy devoted to public expenditures. The straightforward formula for calculating the government spending-to-GDP ratio is: Government Spending / GDP * 100
To obtain the ratio, divide the total government spending by the GDP and multiply the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. This formula allows for a standardized representation of the size of government spending relative to the overall economy.
Â
Data Sources and Methodologies
Reliable data sources and methodologies are crucial for accurate calculations of government spending and GDP figures. National statistics organizations, like the Bureau of Economic Analysis in the US, produce thorough data on GDP and government expenditure. These agencies employ rigorous methodologies, including surveys, administrative data, and economic models, to estimate and track these variables. Data sources can include government budgets, financial reports, and national accounts.
Â
Interpretation of the Resulting Ratio
The resulting government spending-to-GDP ratio provides important insights and can be interpreted in several ways. A higher ratio indicates a larger share of the economy devoted to government spending, suggesting a significant role for the public sector in resource allocation and service provision. Conversely, a lower ratio implies a smaller portion of the economy allocated to government spending, potentially indicating a more limited government role.
Interpreting the ratio requires considering the broader context, such as economic goals, fiscal policies, and societal priorities. Higher ratios may signal increased government intervention, while lower ratios may indicate a greater reliance on private sector activity. Additionally, variations in the ratio over time may be an expression of changes in the objectives of fiscal policy, in the state of the economy, or its structural makeup.
Â
Historical Trends of Government Spending-to-GDP Ratio
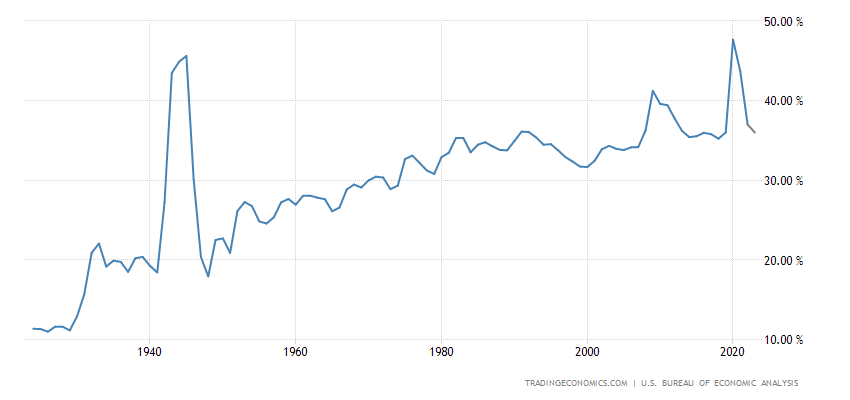
Source: Trading Economics
Â
Historical trends in the government spending-to-GDP ratio showcase the changing dynamics of public expenditures over time. We can spot patterns, movements, and long-term trends in government expenditure by analyzing data from past years. Historical trends help policymakers and economists understand the factors that have influenced government spending, such as economic cycles, policy priorities, and societal needs. We can better understand how the government's involvement in the economy is evolving and how it affects economic results by analyzing these patterns.
Â
Implications and Policy Considerations
A high government spending-to-GDP ratio can impact fiscal health and debt sustainability. Excessive government spending relative to GDP can lead to budget deficits, increased public debt, and potential challenges in servicing that debt. It is crucial to carefully manage government spending to maintain fiscal health, ensure debt sustainability, and avoid adverse consequences on long-term economic stability.
The optimal level of government spending on GDP is a subject of debate. Different economic theories and policy perspectives argue for varying degrees of government intervention. Maintaining the right balance is very crucial. Too little government spending can lead to underinvestment in crucial areas, while excessive spending can crowd out private investment and hinder economic efficiency. When deciding on the proper level of government expenditure, decision-makers must take into account the distinctive requirements, priorities, and financial conditions of their nation.
The government spending-to-GDP ratio has policy indications for economic growth, inflation, and income distribution. Government spending influences economic activity and promotes growth, but it must be balanced to avoid inflationary pressures. Moreover, the allocation of government spending across different sectors and programs can impact income distribution and social equity. Careful policy amendments are necessary to ensure that government spending supports sustainable economic growth, maintains price stability, and promotes a fair and inclusive society.
Â
Conclusion
Understanding the magnitude of the US government's spending-to-GDP ratio offers valuable insights into the economic health of the nation. This ratio serves as a key indicator, helping policymakers and citizens gauge the effectiveness of fiscal policies, analyze historical trends, and make informed decisions. By monitoring this ratio, we ensure responsible allocation of public funds and sustainable economic growth. Continued research and analysis in this area will further enhance our understanding of the dynamics between government spending and GDP, empowering us to shape a prosperous future. Â



