Understanding the US Military Budget is of utmost importance in comprehending the country's defense capabilities and the allocation of financial resources. With defense spending playing a crucial role in national security, it is essential to delve into the details of the US Military Budget. In addition to underlining the budget's importance and effects on the United States, this blog post seeks to give a thorough study of it. Analyzing the complexities of defense expenditures can help us understand the country's defense goals, strategy, and effects on its military.
Understanding the US Military Budget
The US Military Budget refers to the financial allocation made by the federal government of the United States to fund its defense operations. It stands for the amount of money used to support and improve the military capabilities of the country, uphold national security, and protect its welfare both at home and abroad. The budget includes a large number of charges for employees, operations, equipment, research and development, and other connected expenses.
Growth of US Defense Spending by Year
The US Military Budget has a rich historical context. Its roots may be found in the founding of the country when the Constitution granted Congress the power to finance the common defense. Wars, geopolitical developments, and changes in national security goals have all had an impact on the varying levels of defense spending over time.
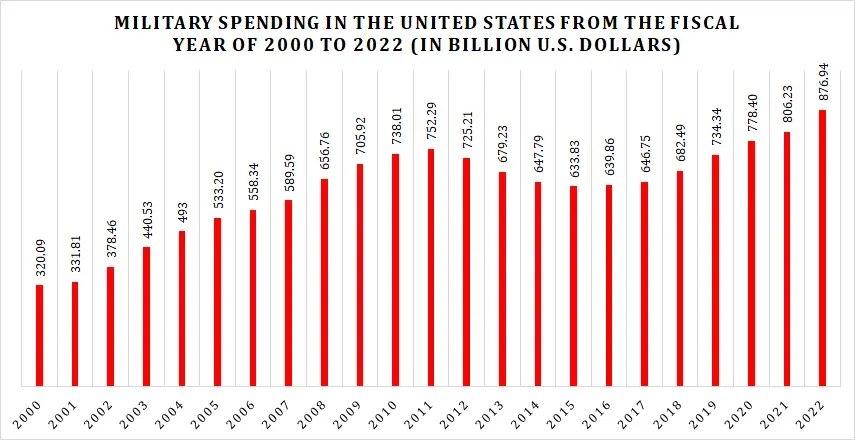
Since World War II, defense spending has witnessed significant growth. Military spending expanded during the Cold War as the US and USSR engaged in an arms race. Under the Reagan administration, defense expenditure reached its pinnacle in the 1980s, with a concentration on scientific improvements and military modernization.
In recent years, defense spending has remained substantial, although it has fluctuated due to changing geopolitical landscapes and budgetary considerations. Spending on defense has rushed in response to the 9/11 attacks and the subsequent wars in Afghanistan and Iraq to sustain counterterrorism activities and enhance homeland security measures.
Comparison of US Military Budgets with Other Countries 2023
The US military budget has surpassed the total defense expenditures of numerous other countries to become the largest in the world. The United States' position as a major military power and dedication to preserving military dominance is reflected in this significant allocation. The comparison with other countries' military budgets highlights the scale and magnitude of US defense spending.
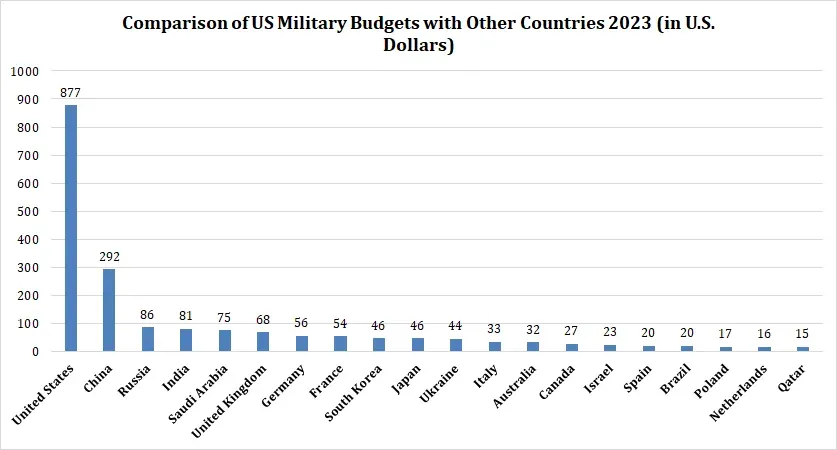
While exact figures vary annually, the United States consistently allocates a significant portion of its federal budget to defense. Comparatively speaking, nations like China and Russia have far smaller defense expenditures yet have recently increased their military spending. The US outspends these countries by a wide margin, reflecting its dedication to sustaining a technologically advanced military force capable of addressing a wide range of security threats.
US Military Spending Percentage of GDP
US military spending as a percentage of GDP varies over time but generally hovers around 3-4%. As per information found in Wikipedia, the United States reserved over 3.5% of its GDP for defense spending in 2023. This figure demonstrates the significant financial commitment the country makes to its military capabilities relative to its overall economic output. The percentage highlights the priority placed on national security and maintaining a strong defense posture. It is crucial to remember that this proportion may change based on a range of variables, including prevailing economic conditions, geopolitical developments, and adjustments to defense objectives and plans.
Breakdown of Defense Spending
Major Components of the US Military Budget
The US Military Budget comprises several major components that collectively contribute to maintaining and enhancing the country's defense capabilities.
Personnel Expenses: A significant portion of the budget is allocated to personnel expenses, covering the salaries, benefits, and training of military personnel. This comprises those serving on active duty, reservists, and civilian staff workers employed by the Department of Defense. The investment in personnel ensures the recruitment, retention, and development of highly skilled individuals to support the military's operations.
Operations and Maintenance Costs: Operations and maintenance expenses encompass the day-to-day functioning of the military. This component pays for a variety of expenses like the upkeep and repair of military infrastructure, tools, and bases, including charges for training exercises, supplies, and support services. It ensures that the military remains operationally ready and capable of effectively executing its missions.
Procurement and Acquisition: Funds allocated to procurement and acquisition are dedicated to acquiring new weapons, vehicles, aircraft, and other defense systems. This component enables the military to modernize its equipment, replace outdated assets, and acquire advanced technologies. Investments in procurement and acquisition help to enhance the military's capabilities, effectiveness, and readiness for future challenges.
Research and Development: Research and development (R&D) expenditures play a crucial role in maintaining technological superiority and innovation within the military. The money set aside for R&D encourages the creation of innovative military technology, weapons systems, and tactics. It enables the military to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, adapt to emerging threats, and address evolving security challenges.
Other Miscellaneous Expenses: The US Military Budget also includes various other miscellaneous expenses. These can include healthcare for military personnel, housing allowances, support for veterans, and contributions to international military alliances and peacekeeping missions. While individually smaller in scale, these expenses collectively contribute to the overall functioning and support of the military.
Percentage Allocation to Each Component
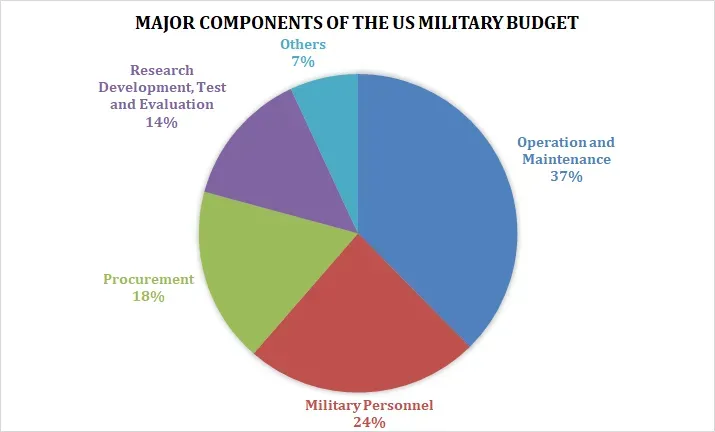
The percentage allocation to each component within the US Military Budget varies annually and is influenced by strategic priorities and budgetary considerations. Although they account for between 50% and 60% of total spending, operation and maintenance costs, and employee remuneration often account for the largest share of the budget. Procurement and acquisition typically receive around 20-30%, while research and development receive around 10-15%. Other miscellaneous expenses constitute a smaller percentage of the overall budget.
Examples and Explanations of Key Expenditures
Key expenditures within the US Military Budget can vary depending on specific needs and priorities. For instance, examples of personnel expenses include salaries, healthcare benefits, and educational support for service members. Operations and maintenance costs may encompass the maintenance of military bases, fuel expenses, and training exercises.
The purchase of new aircraft carriers, fighter fighters, submarines, and other cutting-edge military systems accounted for enormous procurement and acquisition costs. Investments in research and development help with efforts including the creation of cutting-edge military technology, cybersecurity programs, and improvements in artificial intelligence and autonomous systems.
Other miscellaneous expenses may include funding for military healthcare programs, construction and infrastructure projects, support for veterans' benefits and services, as well as contributions to international peacekeeping missions and alliances like NATO.
Factors Influencing the US Military Budget
The allocation and growth of the US Military Budget are influenced by a variety of factors that shape defense spending decisions.
National Security Considerations
The primary factor driving the US Military Budget is the need to ensure national security. The budget reflects the resources required to protect the country's sovereignty, deter potential adversaries, and respond to various security threats. National security considerations encompass the assessment of current and emerging risks, intelligence assessments, and the determination of the military capabilities necessary to address those threats effectively.
Defense Strategy and Objectives
The US Military Budget is shaped by defense strategy and objectives set by policymakers. These strategic considerations define the country's military priorities, the desired force structure, and the missions it aims to accomplish. The budget allocation aligns with the defense strategy, emphasizing areas such as force modernization, maintaining readiness, and investing in capabilities required to meet evolving challenges.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology play a significant role in defense spending decisions. The need to stay ahead in military technology drives investments in research and development, ensuring that the military remains technologically superior. The budget allocation reflects efforts to acquire cutting-edge systems, develop emerging technologies, and maintain a competitive edge in areas like cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and advanced weaponry.
Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical considerations influence defense spending, as the United States responds to global security dynamics and regional threats. Changes in international relations, the emergence of new powers, conflicts, and alliances all impact defense priorities. Geopolitical factors drive decisions on force deployments, investments in regional security partnerships, and the allocation of resources to address specific hotspots or strategic areas of interest.
Domestic Politics and Public Opinion
Domestic politics and public opinion also shape the US Military Budget. Defense spending decisions are subject to political debates, budgetary constraints, and competing priorities within the government. Public opinion regarding the appropriate level of defense spending and perceptions of national security threats influence policy discussions. Balancing defense needs with other domestic priorities, such as healthcare, education, or infrastructure, is a consideration that policymakers must navigate.
Implications and Impact of Defense Spending
The capabilities and preparedness of the military are directly impacted by the defense budget. Ample finance makes it possible to acquire cutting-edge weaponry, create cutting-edge technology, and educate troops. It guarantees that the military is always ready to respond to threats, uphold deterrence, and defend interests in national security.
Economic Effects
Job Creation and Employment: Defense spending has a significant impact on the economy by creating jobs and supporting employment opportunities. The defense sector relies on a vast network of suppliers, contractors, and manufacturers, generating employment across various industries. Defense-related projects, such as military base construction or weapon system production, stimulate local economies and provide a stable source of employment.
Defense Industry Growth: Defense spending contributes to the growth of the defense industry, which encompasses manufacturers, research institutions, and technology firms. Increasing defense spending promotes creativity, advances technology, and the creation of new defense-related goods and services. This growth in the defense industry can have broader economic ripple effects and stimulate innovation in other sectors as well.
Budgetary Implications: Defense spending has implications for the overall budget and fiscal health of a country. Budget deficits caused by high defense spending may require higher government borrowing or the reallocation of funding from other programs, including education or healthcare. Balancing defense priorities with other societal needs requires careful consideration to maintain fiscal responsibility and ensure a sustainable budget.
Criticisms and Debates Surrounding Defense Spending
Opportunity Costs: One criticism of defense spending is the concept of opportunity costs. The funds allocated to defense could be potentially used for other pressing needs such as infrastructure, healthcare, or education. Critics argue that excessive defense spending may divert resources from other sectors that could also contribute to national well-being.
Effectiveness and Efficiency Concerns: Debates exist regarding the effectiveness and efficiency of defense spending. Some argue that increases in defense budgets do not always translate into improved military capabilities or better security outcomes. Wasteful expenditure, cost overruns on defense programs, and the requirement for more control and accountability in defense procurement procedures are all causes for concern.
Conclusion
The US Military Budget plays a crucial role in maintaining the country's military supremacy and national security. The US government ensures that its armed forces are constantly well-equipped and prepared to address a range of security concerns by investing in personnel, operations, procurement, and research.
Understanding the intricacies of the US Military Budget provides insights into defense spending priorities, the impact on the economy, and the ongoing debates surrounding its allocation. By continuing to evaluate and discuss defense spending, policymakers, and the public can work together to strike the right balance between national security requirements and other societal needs.

