Countries like Japan and China play a critical role in the arena of global economics as significant purchasers of US debt. Their purchases of US Treasury bonds have long-term stability for the US economy. Have you ever considered the consequences of Japan and China stopping purchasing US debt? We will talk about potential consequences and how they could affect the global economic environment in this blog article.
Overview of Japan and China as Buyers of US Debt
-
Japan's Historical Role as a Buyer of US Debt
For many years, Japan has been a significant buyer of US debt. There are several reasons why Japan has invested heavily in US debt:
- Stability and Safety: Japan has traditionally viewed US Treasury securities as a safe and stable investment option. The American economy is powerful and durable, its financial system is tightly managed, and it has a remarkable track history of paying off its debts. Japanese investors have sought the security and reliability offered by US Treasury securities.
- Trade Imbalances: Japan has historically had a trade surplus with the United States, meaning it exports more goods to the US than it imports. As a result, Japan accumulates US dollars, and one way to invest those dollars is by purchasing US Treasury securities. This allows Japan to utilize its surplus funds and maintain a balance in its foreign exchange reserves.
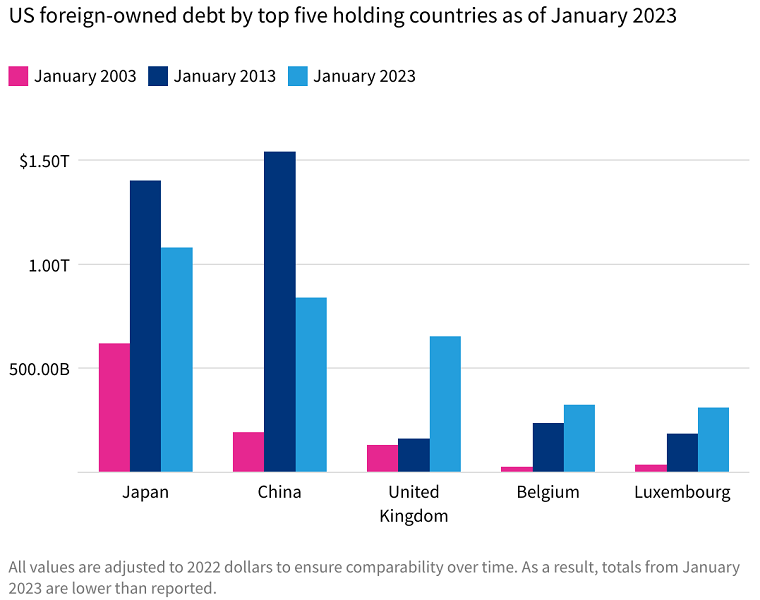
The current level of Japanese holdings of US debt varies over time based on economic conditions, government policies, and market factors. Japan is the largest foreign holder of US Treasury securities valued at 1.1 trillion dollars, according to the US Department of Treasury's record in December 2022.
-
China's Historical Role as a Buyer of US Debt
China has also acquired a sizeable quantity of US debt over the years. Here are some reasons for China's investment in US debt:
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: China's expanding foreign exchange reserves are mostly because of its trade surplus with the US. To diversify its holdings and prevent evolving too dependent on one single currency like the US dollar, China invests a portion of its reserves in US Treasury securities.
- Currency Stability: China has a vested interest in maintaining stability in its currency, the yuan. By investing in US Treasury securities, China helps to stabilize the yuan's exchange rate by managing the supply and demand for dollars.
The current level of Chinese holdings of US debt also fluctuates based on various factors. According to the data of the US Department of Treasury in December 2022, China is among the largest foreign holders of US Treasury securities, with a substantial amount of 867.1 billion dollars invested.
-
Combined Impact of Japan and China as Major Buyers
Japan and China together have a considerable effect on the US and international financial markets as key purchasers of US debt. Here are some key points:
- Financing US Debt: The purchases of US Treasury securities by Japan and China help to finance the US government's budget deficits. By buying US debt, these countries provide the necessary funds that the US government requires to meet its financial obligations like infrastructure spending, defense, and social programs.
- Interest Rates: The substantial demand for US Treasury securities from Japan and China influences interest rates in the United States. When these countries buy US debt, they increase the demand for these securities, leading to lower interest rates. This can have a positive consequence on borrowing costs for the US government, businesses, and consumers.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Japan and China's investments in US debt can also impact currency exchange rates. When these countries purchase US Treasury securities, they effectively increase the demand for US dollars, which can strengthen the dollar relative to their currencies.
Source: US Department of Treasury
Potential Consequences If Japan and China Stopped Buying US Debt
-
Immediate Impact on the US Treasury Market
- Reduced Demand for US Treasury Bonds: If Japan and China were to stop buying US debt, there would be a significant reduction in demand for US Treasury bonds. Both countries have been major purchasers of these securities, and their absence would lead to a decline in demand.
- Increase in Yields and Interest Rates: The reduced demand for US Treasury bonds would put upward pressure on yields and interest rates. With fewer buyers in the market, the US government would need to offer higher yields to attract other investors. This would result in increased borrowing costs for the US government.
-
Effects on US Government Borrowing Costs
- Higher Borrowing Costs for the US Government: With increased yields and interest rates, the US government would face higher borrowing costs. This would have implications for its ability to fund its budget deficits and finance various expenditures, including infrastructure projects, defense, and social programs.
- Implications for the Federal Budget Deficit: Higher borrowing costs would widen the federal budget deficit. The US government would need to allocate more funds towards servicing its debt, leaving fewer resources for other priorities. This could lead to increased pressure to reduce spending or raise taxes to manage the deficit.
-
Impact on the US Dollar and Global Economy
- Depreciation of the US Dollar: The reduction in demand for US Treasury bonds by Japan and China could lead to a depreciation of the US dollar. Both nations have considerable amounts of US dollars; if they sold off their holdings, the number of dollars available on the foreign exchange market would increase, depressing dollar value.
- Effects on International Trade and Currencies: A weaker US dollar would have implications for international trade. It could make US exports more competitive, potentially boosting American industries. On the other side, import costs would rise resulting in increased inflation and having a consequence on consumers' purchasing power. Additionally, other currencies may strengthen the US dollar, impacting exchange rates and trade relationships between various countries.
-
A Shift in Global Economic Power
- Changes in Economic Influence and Relationships: If Japan and China were to significantly reduce or stop buying US debt, it could result in a shift in global economic influence. Other countries may step in to fill the gap left by Japan and China, altering the dynamics of economic relationships. The United States may need to seek alternative sources of financing its debt, potentially leading to new alliances or partnerships.
- Potential for Other Countries to Fill the Gap: The reduced demand from Japan and China could create opportunities for other countries to increase their holdings of US debt. This may include nations with considerable foreign exchange reserves or those seeking to develop stronger commercial connections with the United States. It may lead to a redistribution of economic power and influence among nations.
Possible Strategies and Responses
-
US Government Actions
- Policy Adjustments to Attract Other Buyers: The US government could implement policy adjustments to attract alternative buyers of US debt. This might include offering more attractive yields, introducing new financial instruments, or implementing incentives for investors. The goal would be to diversify the investor base and mitigate the impact of reduced demand from Japan and China.
- Implications for Fiscal and Monetary Policies: The US government may need to consider adjustments to its fiscal and monetary policies in response to reduced demand for US debt. This could involve reassessing the budget deficit, exploring alternative funding sources, or making changes to interest rate policies to manage borrowing costs.
-
Economic Impact on Japan and China
- Consequences for Their Economies and Currencies: The reduced investment in US debt by Japan and China would have economic consequences for both countries. Japan's foreign exchange reserves may vary, which might direct an expansion in the value of its currency, the yen. While maintaining the stability of its currency, the yuan, China may encounter difficulties managing its foreign exchange reserves.
- Potential Alternatives for Investment: With less investment in US debt, Japan and China may seek alternative investment opportunities. By purchasing additional foreign assets, such as bonds from other nations, or increasing their interests in home businesses, they might diversify their holdings. They might also explore investments in infrastructure projects or strategic industries to support their economic growth.
-
International Cooperation and Negotiations
- Diplomatic Efforts to Address the Situation: The situation could prompt diplomatic efforts between the United States, Japan, and China to address the potential consequences of reduced investment in US debt. High-level negotiations and dialogues might focus on finding mutually beneficial solutions to maintain stability in global financial markets and address concerns related to economic impacts.
- Collaborative Solutions and Agreements: International cooperation could lead to collaborative solutions and agreements. For example, the United States might engage in discussions to address trade imbalances and create incentives for Japan and China to continue investing in US debt. Additionally, countries could explore mechanisms to enhance economic cooperation and financial stability, such as currency swap agreements or joint investment initiatives.
Conclusion
Understanding the potential consequences of Japan and China stopping their purchases of US debt is essential for policymakers and economists alike. The consequences on the US Treasury market, government borrowing costs, the US dollar, and the global economic landscape cannot be ignored. Proactive measures and international cooperation are necessary to navigate the challenges that may arise if Japan and China decide to change their investment strategies. By staying informed and prepared, we can work towards maintaining stability and fostering a resilient global economy.